International
Universal flu vaccine for mankind
Influenza virus remains to be a curse to human population due to its dubious antigenic drift and shift properties. There are many instances of havoc cause by flu in the past but still the remedies available are not reliable to protect the future owing to its unpredictable evolving nature. Out of all the types of influenza, the type A has the ability to cause both epidemic and pandemic. Recently, an international group of researchers from universities of Aston, Lancaster and Complutense in Madrid have designed two universal flu vaccines; one against globally known influenza A subtypes whereas other is against US specific subtypes. These new generation vaccines are based on conserved potential immunogenic influenza A virus epitopes which were identified using immunoinformatics. The ensemble epitopes can activate both CD8+ and CD4+ T-cells of human immune system, thereby producing cross protective immunity against multiple emergent influenza subtypes. The USA-specific vaccine could provide protection against 95% of the available subtypes present in US with population protection coverage (PPC) over 96%, on the contrary, the universal one have PPC of over 97% and could protect against 88% of globally present flu in a single shot. The researchers speculate that the vaccines will provide protection to the next year seasonal flu with a very high likelihood of success.
(Bioinformatics, 2016; btw399 DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btw399)
A catechize on RNA world theory
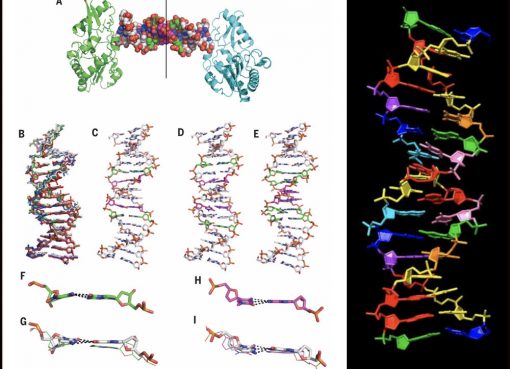
The RNA world theory postulates that all current life on Earth have been evolved from ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules. Thus, proteins and DNA are also inventions of RNA world. Leading scientists from The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have challenged the RNA world hypothesis and forwarded an alternative to it. The study done by TSRI scientist published in the journal Angewandte Chemie offers evidence that RNA and DNA have evolved simultaneously and independently rather than transition of RNA to DNA. It is quite perplexing, whether RNA theory holds true, if yes then definitely there may be cases of RNA nucleotide mixed in DNA backbone producing heterogeneous double strand DNA molecule in one or some form of life. It was experimentally proved that RNA-DNA chimeric is significantly instable as compared to Watson-Crick duplex stability which figure out the pitfalls for transition from one homogenous system (RNA) to the other (DNA) without intermediate stable RNA-DNA chimeras. This form of instability suggests co-evolution of RNA and DNA independently. Moreover, Ramanarayanan Krishnamurthy, one of the authors of this new study stated that this is not the first time the RNA world has been criticised but chimeric instability has forwarded new clues to the modern scientific community and also added that it is very arduousness to conclude how life began on earth but by gaining facts and figure science can go deep into the biology of life.
(Angewandte Chemie 55, 13204-13209, 2016)
Gut bacteria can squash kidney stone
Hyperoxaluria is an indication of kidney stones which thereby increases the risk for various kidney diseases and kidney failure. The building blocks of kidney stones is a complex of oxalate and calcium forming calcium oxalate. Researchers from University of Chicago have discovered that colonization of probiotic potential gut bacteria Oxalobacter formigenes can reduce the risk of kidney stones. Though it is known that human intestinal cells are involved in oxalate balance and gut Oxalobacter formigenes utilizes oxalate as sole energy source but the exact mechanism was not obvious. This recent study revealed that O. formigenes possesses certain bioactive factors having molecular mass of 10-30 kDa that induces oxalate transport in intestinal cells through mechanisms including PKA signalling pathway with the involvement of SLC26A6 protein transporter. By this mechanism there is increase secretion of oxalate by intestinal cells whereby decrease in urinary excretion. The team further validated in O. formigenes treated hyperoxaluria mice model that showed significantly increased (42%) colonic oxalate secretion and significantly reduced (32.5%) urinary excretion. Thus, it can conclude that both the O. formigenes and its derived bioactive factors have potential therapeutics application to prevent kidney stone and associated diseases.
(Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 2016; doi: 10.1681/asn.2016020132)
A pathway to eternal life
Russian Chemist Anatoli Brouchkov asserts he is experiencing eternal life after injecting 3.5 million years old primordial bacteria. In 2009, Dr. A. Brouchkov discovered the bacteria named Bacillus F in Siberian permafrost which was alive for millions of years. Promising experimental findings on plants, human blood cells, mice and fruit flies insisted self-injection of inactivated bacterial culture. Thereafter, the scientist claims that he could work longer and never experienced flu for last couple of years. The hypothesis behind it was that the permafrost is thawing gradually and there is very likelihood of mixing these bacteria with drinking water of Yakut people, a native of Siberian, who have longer life span than the people from neighbouring nations. However, Dr. Brouchkov stated that exact mechanism is still under veil and have to be proved experimentally, clinically and statistically.
Treat Diabetes with Artificial Pancreas
The first automated insulin-delivery device, called the MiniMed 670G from Medtronic is approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It measures glucose levels at every five minutes interval and automatically administers insulin as needed for what it is known as ‘Artificial Pancreas’. The basic components of MiniMed 670G include an insulin pump connected to a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) sensor called Guardian sensor, inserted under the skin, a transmitter and a glucose meter. In Auto Mode the device senses the glucose level from CGM every five minutes and automatically delivers the adjusted level of insulin to maintain 120mg/dl. The device is developed by Medical Company Medtronic which is going to be launched in the spring of 2017. Currently approved system is for patients of 14 years and over suffering from Type 1 diabetes, although a study is underway for 7-13 years old children.
(https://diatribe.org/drugdevice-name/medtronic-minimed-670g)
A vital factor for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration
Researchers from Finland have discovered a key transcriptional factor for tremendous regenerative properties of adult skeletal muscle after damage. The factor is identified to be the prospero-related homeobox 1 (Prox1), documented to have role in development of liver, pancreas, heart, lymphatic vessels and lens in the eye during fetal life. Skeletal muscle stem cells called satellite cells differentiate to myofibres only when Prox1 gene is active and highly expressed. The group also provided evidence that Prox1 is essential for gene program of adult slow muscle fibres having high endurance capacity and metabolic activity. The factor Prox1 is critical in NFAT and Notch signalling pathway for regulation of slow muscle fibre type and myoblast differentiation. However, one of the previous studies has reported a dark side of Prox1 showing major role in development of colorectal cancer.
(Nature Communications, 7: 13124, 2016; doi: 10.1038/ncomms13124)
A novel gene therapy to heal Alzheimer’s disease
The occurrence of Alzheimer’s disease is hiking day-by-day with no permanent remedies to uproot the cause. The basic cause of Alzheimer’s disease is formation of plaque due to deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides causing neurodegeneration. Moreover, Aβ plaques also act as bedding for defective variants of tau protein leading to inflammation and destruction of neurons. An advanced scientific experiment published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reports a novel gene therapy that can end the cause of Alzheimer’s disease in its infancy. The therapy was given to the brain of mice model and the gene included in this study is a transcription regulatory gene known as peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptorγ coactivator1α (PGC1α) involved in energy metabolism. In this experiment, lentiviral vector encoding PGC1α gene was delivered to the cortex and hippocampus of genetically engineered mice that has ability to generate higher level of Aβ. Four months post-delivery of PGC1α gene, the transgenic mice showed no memory impairments and there was significant reduction in Aβ plagues formation. The PGC1α gene works by blocking the expression of βAPP cleaving enzyme (BACE1), the key molecule involve in Aβ formation. This new finding suggests that PGC1α gene holds promising therapeutic intervention to overcome Alzheimer’s disease in near future.
(PNAS, 2016; doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606171113)
National
Indigenous expression system to cut disease treatment cost
Now the cost of insulin, Hepatitis B vaccine could be cut down to minimal as for the first time Indian scientists have developed indigenous expression system to produce medicinal value recombinant protein. A group of scientist from Institute of Microbial Technology (IMTECH), Chandigarh, have devised a new expression system with fission yeast to produce recombinant protein. So far, Indian biotech companies have to depend on Pichia expression system, patented by foreign scientist, to produce therapeutics protein which adds extra in production cost. The team has successfully produced Hepatitis B vaccine at laboratory scale using in-house expression system and claims that it will reduce the cost of therapeutics protein like insulin, streptokinase etc. by four to five times.
India could be a hotbed in primate evolution
A study published in the Journal of Human Evolution reported fossils of extinct primates that lived in India million years ago. Evolutionary anthropologists of the study found the gray mouse lemur size fossils in the coal mine of Gujarat. The finding consist a set of 25 arm, leg, ankle and foot fossils which were around 54.5 million years old. Probably, it could be the common primate ancestor which may lead to the evolution of present day primate family. Previous studies on fossils suggested that early primates were evolved from African continent but this new finding has opened a new window that India may be also a part of early evolution of primates.
(Journal of Human Evolution, 99: 25-51, 2016)
Genome of the Queen of Herbs is decrypted
For the first time, a team of scientists from India have drafted the genome of Tulsi, the scared herbs. Ocimum tenuiflorum (Tulsi) is regarded as the Queen of Herbs because specialized metabolites produced by it as part of defense mechanisms have therapeutic properties like antioxidant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer. And since time immemorial it has been prescribed for bronchitis, malaria, diarrhea, dysentery, etc. The team successfully assembled 61% (374 Mb) of the whole genome which is 612 Mb in size and by transcriptomics approach identified potential genes that confer medicinal properties to the plant. The study concluded that the whole genome of Tulsi will provide better understanding of mechanism how these metabolites have achieved therapeutic potential.
(BMC Plant Biology, 15:212, 2015; doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0562-x)
Assam is first to launch Bedaquiline
Assam is being anguished continuously by tuberculosis. Moreover, the cases of multi-drug resistance tuberculosis are expanding gradually. Bedaquiline (BDQ), a prodigious drug, to fight against multi-drug resistance tuberculosis was first launched in Assam in the country and in Asia. The drug is contributed by USA which is USFDA approved. Though the drug is expensive but Jansen, US based company has provided free of cost to the hospitals of Guwahati, New Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Ahmedabad with limited dosages.
(http://www.biospectrumasia.com/biospectrum/news/223837/indias-assam-launch-miracle-tb-drug)
Zikavac is ready for phase-I trail
Outbreaks of Zika fever in the globe are making headlines in many countries. Till date, around 18 international companies and institutions are trying to develop vaccine against Zika virus and out of all India’s Bharat Biotech Company is one of it. Novel Zika vaccine, ‘Zikavac’, is an inactivated vaccine developed by the company and already it has completed the pre-clinical toxicological studies in animal model. The vaccine is now ready to go for phase-I trail which will be done in 100 human volunteers.
Vaccine to eliminate tapeworms in pigs
Cysticercosis is one of the tropical diseases caused by tapeworm Taenia solium, a zoonotic parasite. Pig act as intermediate host for the parasite and humans are infected due to consumption of eggs present in raw pork, undercooked pork or contaminated vegetables and water. Recently, Hyderabad city-based company, Indian Immunologicals Limited (IIL) in collaboration with many international institutions have designed and launched a vaccine to combat cystecercosis in pig. It is a recombinant vaccine named as ‘Cysvax’ which will stop the parasite to form cyst in pig. The company also claims that it has the potential to decrease the degree of epilepsy in humans.